Welcome!
By Felipe Lamounier, state of Minas Gerais, Brazil – powered by 🙂My Easy B.I.
In this post we will learn how to identify Process Chains (RSPC) in SAP BW with recurring errors in a given period.
📑 Table of Contents:
Introduction
Identifying Process Chains in SAP BW with recurring errors aims to ensure governance of the BW environment and efficient resource management. This occurs because improperly executed chains, whether due to obsolescence or undetected errors, consume unnecessary system resources, increase execution logs and negatively impact the speed at which information is returned.
Roadmap
- First step is to find the distinct list of Metachains of Process Chains (RSPC) that had 1 or more errors in the period (in our case, 65 days)
- Select all execution logs of the distinct process chains returned in item 1
- Discover which chains have recurring errors through the average of total errors
🗒️Step by Step
Go to transaction “ST13” (Analysis & Monitoring tool collection). In “Tool name” enter “BW-TOOLS“:
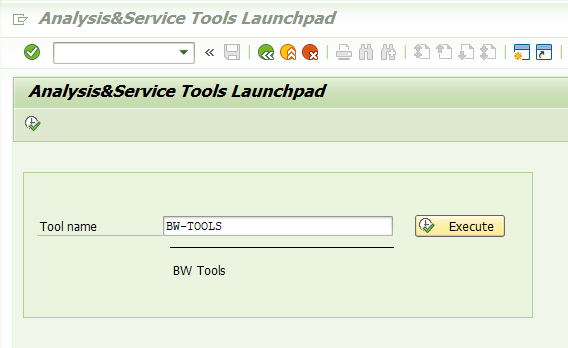
Choose the option “Process Chain Analysis“:

Click the “Process Chains” button.
Enter the desired period in “Start Date.“
In “Do not display Chains in Status“, check the “Green” and “Yellow” options.

Please wait a few minutes for the list to be returned. Filter the column “Main” = “X”.
Only the main Process Chain will be filtered when it is unique, or the Meta Chain.

Export the filtered chains to a spreadsheet:

The next step is to select the distinct Process Chains. Select the “Chain” column. Click on the “Data” tab and then “Remove Duplicates“. Copy the chains names.

Go back to the “ST13” transaction and click the “Selection” button. A new box will open.
In “Chain-ID“, paste the distinct Process Chains obtained in the previous step.
In “Do not display Chains in Status“, select only the “Yellow” option:

Click on “Change Layout” and include the “Errors” column:
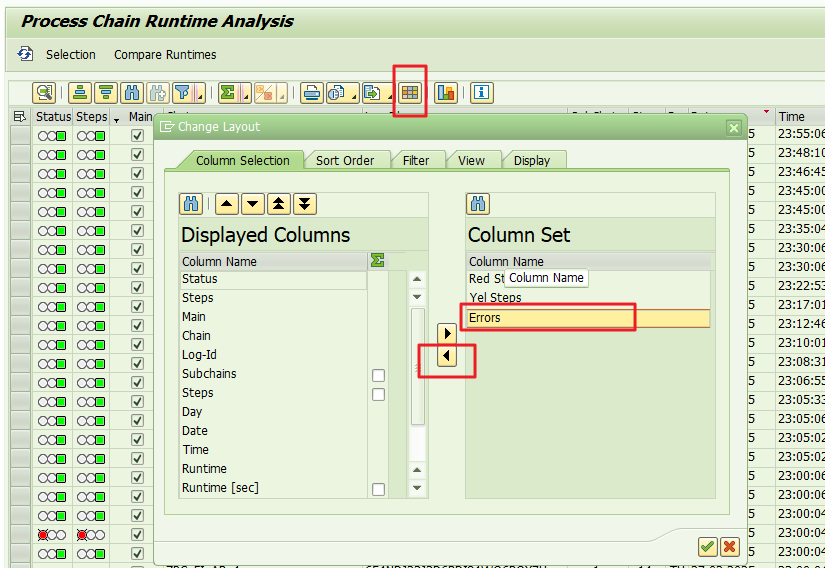
Select the “Errors” column, click on Total ∑ and select “Mean Value” (Average).

Select the “Chain” column and click on “Subtotals“:

The average errors will be grouped by Process Chains. When the average is greater than or equal to 1, it should be reviewed as it has recurring errors.
Export the list to Excel, delete the rows with an error average equal to 0, and work on the remaining Process Chain relationships.
Evaluate each chain individually. If a particular chain has been running with errors every day for more than 60 days, it is likely that this process chain can be removed from scheduling. Conduct the analysis, adjust, and/or stop the scheduling.

🎦Step by Step Video
Video in Portuguese with subtitles in English, German, Russian, French, Spanish and Chinese.
Conclusion
By identifying recurring errors across multiple SAP BW Process Chains at once, you streamline troubleshooting, reduce wasted resources, and maintain a healthy BW environment. Following the outlined steps—finding Metachains with errors, filtering for unique chains, calculating error averages, and focusing on repeated issues—leads to more efficient governance, frees up system resources, and improves overall data delivery performance.
Feel free to leave any questions, suggestions, or comments in the comments section below, at the end of the page.
Keywords: SAP BW process chains; Recurring errors; Process chain failures; Mass identification; RSPC error logs; SAP BW governance; ST13 transaction; BW error analysis; Process chain troubleshooting; Error resolution steps; Identifying SAP BW Process Chains with Recurring Errors; How to identify SAP BW process chains with recurring errors; Mass error analysis in SAP BW process chains; Best practices for recurring error resolution in SAP BW; Transaction ST13 for SAP BW error troubleshooting; Governance strategy for SAP BW process chain failures; Improve SAP BW performance by reducing recurring chain errors
Did you like the content? Want to get more tips? Subscribe ↗ for free!
🔭See Also:

Want to learn more? Access our area 🎓🚀Training&Education↗
Follow on social media: